Types of Hearing Loss
When any part of the hearing system is unable to function, the result is hearing loss. There are several types of hearing loss:
Conductive Hearing Loss
Conductive hearing loss is caused by damage to the outer or middle ear. With a conductive loss, sound waves are blocked as they move through the outer or middle ear. Since the sound cannot be conducted efficiently, the sound energy that reaches the inner ear is weaker or softer. A conductive loss can result from infection, excessive earwax buildup, fluid in the middle ear, damage to the middle ear bones, a perforation of the eardrum or a foreign body in the ear canal.
Signs/symptoms may include: 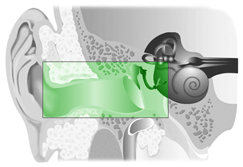
- Perceiving speech and other sounds as faint or muffled.
- Ear pain or discharge from the ear.
- Redness or swelling of the outer ear.
- Pressure or fullness in the ear.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensorineural hearing loss is caused by damage to the inner ear. Sound waves travel normally through the outer and middle ear, however, the inner ear is unable to pick up the vibrations or is unable to send the vibrations to the brain. Also called "nerve deafness", it usually occurs in both ears. A sensorineural loss can result from infection, disease, certain drugs, excessive noise, birth defects and aging.
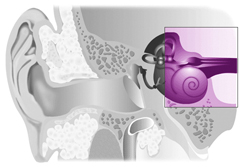
Signs/symptoms may include:
- Perceiving speech and other sounds as distorted or unclear.
- Difficulty hearing certain pitches (usually high pitches).
- Hearing a ringing or buzzing sound that is constant or periodic.
- Difficulty understanding speech in the presence of background noise.
Mixed Hearing Loss
Mixed hearing loss is caused by damage to the outer/middle ear and the inner ear. Typically, sound waves are not conducted efficiently to the inner ear, and once they reach the inner ear the vibrations cannot be picked up or sent to the brain. Therefore, a mixed hearing loss is the combination of a conductive and sensorineural hearing loss.

Signs/symptoms may include:
- See "Signs/Symptoms" under Conductive hearing loss & Sensorineural hearing loss.